Bucket Permissions¶
Bucket owners¶
Developer Buckets¶
All buckets you create are scoped to your developer account. You can always find your currently logged in account with hub whoami.
Organization Buckets¶
Any bucket you create using the HUB_ORG setting will also be shared with Org members.
The following sections will cover how to:
- Create a new Org.
- Create a new Bucket shared with an Org.
- Invite a collaborator to the Org.
Create a new Org¶
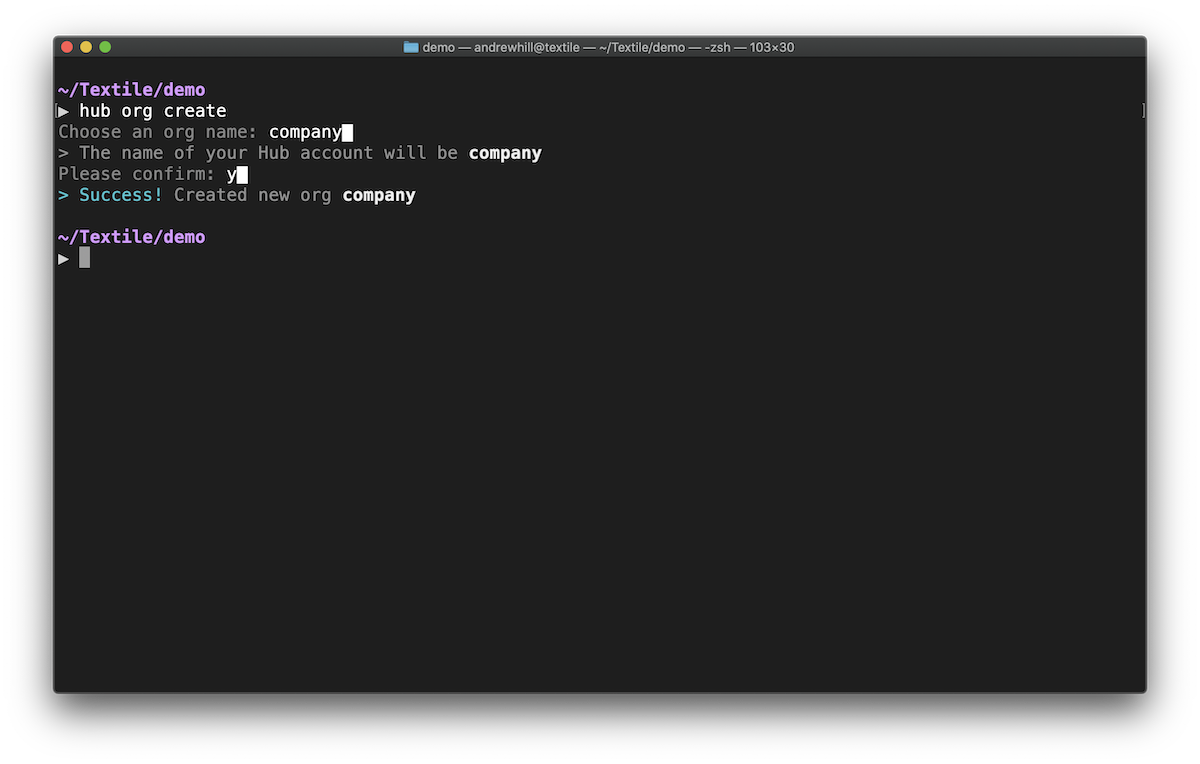
hub org create
Choose an Org name: nasa█
Please confirm: y█
Success
> Success!
You have now created the nasa Org.
Create a new Bucket shared with an Org¶
The default bucket command is simply buck because it's two letters less to type each time. If you prefer, you can still type bucket.
mkdir launchpad
cd launchpad
HUB_ORG=nasa hub buck init
You've now created a new Bucket inside of the launchpad directory and owned by your nasa organization.
Invite a new org member¶
hub org invite
The final step is to invite collaborators to your Org. Once they accept the invite, they'll be able to interact with buckets associated with the Org.
App user Buckets¶
If you're building an app using one of our developer libraries, you can use buckets from inside your apps. Apps generally will create buckets on behalf of each user, meaning the user should retain control of the Bucket metadata and contents.
Bucket Access Roles¶
Buckets can be shared in more ways than organizations.
Multi-writer buckets leverage the distributed nature of ThreadDB by allowing multiple identities to write to the same buckets that are hosted by different Libp2p hosts. Since buckets are ThreadDB collection instances, this is no different than normal ThreadDB peer collaboration.
Path access¶
Read and write access roles are defined in a bucket at any path. Any subpaths automatically inherit the permissions of their parent.
For example, granting read access to your bucket at / would also grant read access to a file that exists at /path/to/foo.jpg.
You can set different access rules within the same bucket by using a combination of paths and specified roles at the path.
Role types¶
| Admin | Users with the ability to modify permissions. |
| Writer | Users allowed update data at the specified path. |
| Reader | Users allowed read data at the specified path. |
| Unspecified | Users with any permissions specified path. |
Authorizing users¶
You can specify new users and their roles by inserting their public key into the bucket access rules. Let's take a look at how we update roles using the CLI.
hub buck roles grant -r writer \
bbaareicookqfgeosr225wwdknmpmvgemydxolzxesu6woxghpulxvizose /path/to
Success
IDENTITY ROLE
* Reader
bbaareicookqfgeosr225wwdknmpmvgemydxolzxesu6woxghpulxvizose Writer
bbaareieyrq92sbfcx2bhbmsfxzj25pi7ldx2vkrtcn6hu3xzi4mpzwqvcy Admin
> Success! Updated access roles for path /path/to
Success! You can see the new user has been added as a writer to the path /path/to and that the bucket creator is still listed as the admin.